2PMreports that 13 of the top 20 direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands are in the fashion and apparel industry. Brands like SHEIN, Chewy, and Gymshark make the shortlist, proving the crushing power fashion brands hold in theecommercespace.
Digital innovation, rising globalization, and changes in consumer spending habits have catapulted the fashion industry into the midst of seismic shifts. But, thanks to rising inflation and supply chain pressures, the fashion sector is more unpredictable than ever.
This guide shares the statistics, trends, and strategies shaping theecommerce fashionmarket in 2023 and beyond, giving you an updated look on where we are and where we’re heading.
Top fashion ecommerce trends in 2023
The above data points offer a wealth of growth opportunities for fashion and apparel retailers—despite the huge shifts in consumer behavior, global trade, and “normal” day-to-day lives for millions around the world.
Below are some of the latestecommerce trendsthat you can work into your long-term fashion sales strategy.
- Personalization is a balancing act
- Into the metaverse
- Brand-building over paid ads
- Sustainability at the forefront
- Social commerce
- The transition back to brick-and-mortar
1. The rise of resale
Secondhand apparel is becoming a global phenomenon. The resale market grew 24% in 2022 alone, and is expected to reach a$218 billion market valuationby 2026.
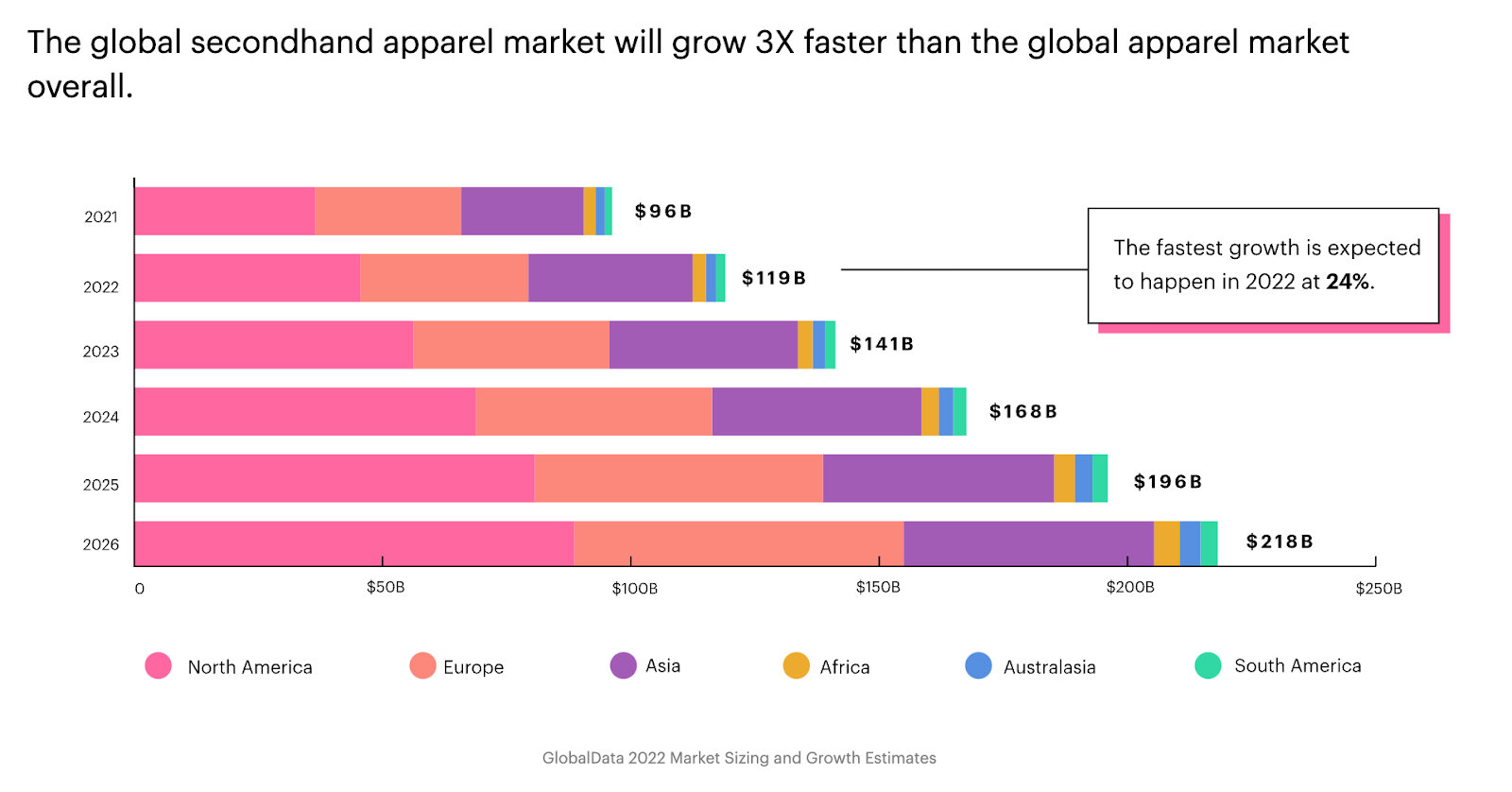
Source:ThredUp
Leading the trend is North American consumers, where the secondhand apparel market has grown eight times faster than the overall apparel market. Technology and online marketplaces are driving this trend, with70%的消费者saying it’s easier now to shop secondhand than it was five years ago.
Secondhand displaced nearly one billion new clothing purchases in 2021 that normally would have been bought new.
—ThredUp
Secondhand displaced nearly one billion new clothing purchases in 2021 that normally would have been bought new.
Fashion brands are taking notice.Dôen, a California-based premium fashion brand, is launching a resale program, called Hand Me Dôen. The program will allow customers to send in pre-owned Dôen products in exchange for store credit.
Dôen will host flash sales throughout the year when the resold product becomes available. The goal of not making resale available all the time is to prevent customers from visiting the site and finding it already picked over.
Sheinis also launching a resale platform in the wake of criticism about its labor practices. Some experts are skeptical about the platform and believe it is simply a way for the company to greenwash its image.
It remains to be seen whether fast fashion brands will be able to capitalize on the resale market in the same way luxury and premium brands have. However, one thing is certain: the resale market is here to stay, and it is only getting bigger.
2.Personalizing the customer journey
Personalization has long been hailed as the secret of modern ecommerce. By showing items a shopper was previously interested in, or retargeting them based on the activity they’ve had with your欧宝体育百家乐, you’re providing a tailored online shopping experience—one that convinces them to buy.
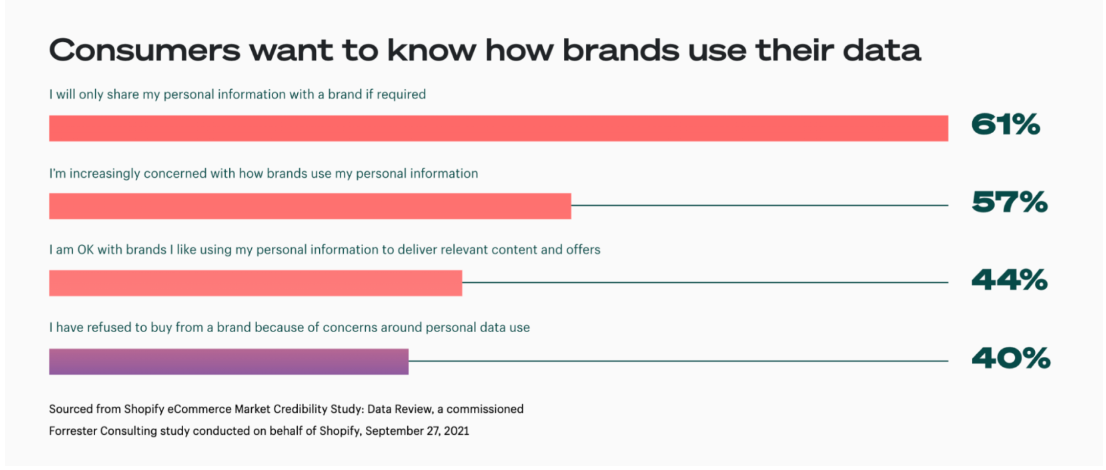
Shopify research shows that 44% of customers are OK with brands using their personal information to personalize messaging and improve the customer experiences, such as product recommendations. But there’s a fine line.
Online shoppers are increasingly concerned about their privacy. Too much personalization can be creepy, hence why brands that over-personalize arethree times more likelyto be abandoned by shoppers.
Culture Kingsis the perfect example of how fashion ecommerce brands can balance under- and over-personalization. Instead of customizing the experience down to “first name” tags on the website, it built four global storefronts to sell in different currencies. The result? More than half of the fashion brand’s revenue now comes from itsecommerce business.
I believe we’ll see more local brands branching out and offering customized shopping experiences for international customers to remain competitive. This will include things like geo-targeted domain names, pricing in local currency, and local product shipping, with the help of third-party distribution or company-owned warehouses.”
—Leanne Lee, Marketer atBlue Bungalow
3. More brands experimenting with the metaverse
The definition of “metaverse” is open to interpretation. The not-quite-defined promise of virtual societies is still in development, though the idea is that people can conduct daily activities—like connecting with friends, playing a game, and purchasing products—by using augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technology.
One type of item that functions both in and out of the metaverse isnon-fungible tokens (NFTs)—unique digital tokens that can only be owned by one person, usually paid for in virtual currency like crypto. Data shows$87.03 millionwas spent on NFTs on January 1, 2022, alone.
Celebrities likeReese Witherspoonwere mocked for predicting, “In the (near) future, every person will have a parallel digital identity. Avatars, crypto wallets, [and] digital goods will be the norm.”
“In everything we do, we’re helping the customer imagine. We want them to imagine being the man in every picture. To imagine us being their stylist. To imagine, ’That could be me wearing those clothes.’ We’re not so much curating content as curating imagination.”
—Kevin Dao, Co-founder and CEO/CCO atORO LA
在现实中,健身服装品牌Armo下ur are experimenting with NFTs in the retail space. ItsSteph Curry collaborationreproduced shoes the basketball star wore when he broke the NBA record as all-time top three-point shooter.
Digital NFTs were released alongside the physical product launch. Owners of the NTFs could virtually wear the shoes in three metaverses: Decentraland, The Sandbox, and Gala Games.
Retailer Forever 21 partnered with Roblox to create virtual fashion ecommerce stores in its metaverse, appropriately named the Forever 21 Shop City. Players run the virtual store as if it was their own, and purchase merchandise for their avatar through the game.
With Forever 21 Shop City, our goal is to expand how we engage with customers, extending our presence and product in new ways.”
—Katrina Glusac, chief merchandising officer at Forever 21
Fast-fashion retailerPrettyLittleThingalso recently began showcasing products on virtual models. The brand posted the news to its Instagram page, turning its new “avatar in the metaverse” concept into a competition to spark conversation.
“Just like Fortnite community inspired Balenciaga’s designs, fashion companies can move towards becoming creative collectives. Each collection can have its own identity within the brand universe, reputation, and community. Collectives can focus on the actual product designs and/or on content creation, with associated royalties based on item/content performance, delivering returns to creators in perpetuity and ensuring that a brand attracts the very top talent.”
—Ana Andjelic, Founder ofThe Sociology of Business
Fashion brands are using Roblox to create immersive experiences for users and reach Gen Z audiences. This is just the beginning for fashion brands in the metaverse. As our world becomes more and more digitized, it’s likely that we’ll see even more brands experiment with NFTs and other virtual reality experiences. It’s an exciting time to be a fashion fan, and we can’t wait to see what brands come up with next.
4. Sustainability at the forefront
The fashion industry is no stranger to criticism. Fast-fashion brands especially are (sometimes rightly) chastised for the methods they use to manufacture and produce inventory.
In light of these criticisms making mainstream news, plus consumers’ increasing commitment to eradicate climate change, some52% of shopperssay they’re more likely to purchase from a company with shared values.
An important value for modern fashion consumers? Sustainability. Statista’s research shows42% of global customerspurchase eco-friendly and sustainable products. Certain countries are leading the trend—online shoppers in Vietnam, India, and the Philippines purchase sustainable products more often.
With people spending more time online, it is going to facilitate faster exchange of that information [about suppliers]. We’ve become more aware of how things that happen in far flung places affect us and the planet. That’s been a real key change we’ve seen.”
—Grace Beverly, Founder ofTALA
Purchasing habits are also shifting off the back of the pandemic. Some65% of customersplan to purchase more durable fashion items, with 71% planning to keep the items they already have for longer. The fashion resale market is booming for this reason—growing11 times fasterthan traditional retail and tipped to reach a $77 billion valuation in the next five years.
Patagonia is one apparel brand with sustainability rooted in its brand values. The retailer actively campaigns for environmental causes, and demonstrates its commitment to sustainability with its Worn Wear program. Shoppers are encouraged to buy and sell used items instead of buying new.
We’re proud to offer our customers a conscious shopping choice with sustainable, affordable pieces that are all handpicked and on trend, but we believe every brand needs to take responsibility, and push themselves to become more circular.”
—Kate Peters, Managing Director ofBeyond Retro
5. More investment in social commerce
Social media plays an integral role in the ecommerce marketing strategy of many online fashion brands. That’s hardly surprising—our smartphone addiction is out of control. The typical social media user now spends about15% of their waking lifeglued to an online networking app.
But the truth is: social media is no longer a place for shoppers to consume new fashion trends. Many social media platforms are evolving their business models to facilitate in-app shopping, helping online retailers reach customers actively in the purchasing frame of mind.
Social commercesales are expected tonearly triple by 2025, withmore than one-thirdof Facebook users planning to make a purchase directly through the platform in 2022.
Unfortunately, most brands are plagued by a single sin. Andy Crestodina, co-founder ofOrbit Media, describes the situation perfectly: “Most branded content is advertising under a thin layer of information or entertainment. Scratch the paint, find an ad. It’s the brand putting itself first.”
Thankfully, fashion and social media are a match made in ecommerce heaven. Even when it comes to explicitly “branded” content, and especially on Instagram.
Social mediaengagement ratesfor global fashion brands are abysmal:
- Instagram: 0.68%
- Facebook: 0.03%
- Twitter: 0.03%
So, what types of content is working for fashion brands? Some 46% of consumers want to watch product videos before they buy. Platforms like TikTok and Instagram are praised for driving sales for large fashion brands since shoppers can visualize the product on a real person. Bonus points if it’s a social media influencer they already trust.
Long gone are the days of celebrities being only someone you’d see on TV. Today, anyone with a passion can become a celebrity in the social media niche—partly due to the rise of entertainment platforms like Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitch.
Beyond influencer marketing on social media, multichannel ecommerce integrates native selling off site to build direct buying paths in the places your audience spends their time. Social media platforms are creating their own commerce features—like Shopping on Instagram, Facebook Shops, buyable pins on Pinterest, and more.
Livestream shopping is also in its heyday. Nordstrom launched its own livestream shopping channel last year. It’s in good company: 81% of companies plan to increase or maintain their investment in livestream selling to drive sales over the coming year.
Why? Because online brands are seeingconversion rates of up to 30%through Facebook and Instagram livestreams, along with lowerproduct return rates.
“My prediction is that in a couple years, the hottest role for a brand to hire is going to be a head of live shopping.”
—Kevin Gould, Co-founder of Glamnetic
6. The transition back to brick-and-mortar
The shopping experience is more complex than ever—especially in the fashion space. Some22% of online returnshappen because the product ordered online looks differently in the flesh. It’s this never-ending challenge that’s driving many fashion brands back into traditional retail.
“未来是电子商务和零售。这是just commerce. So the question becomes, ‘How do you symbiotically integrate both channels?’”
—Hemant Chavan, founder ofBrik + Clik
Data compiled in Shopify’s Future of Commerce report proves omnichannel commerce isn’t disappearing anytime soon. Modern consumers want both online and offline sales channels—and synergy between the two:
- 54% of consumers are likely to look at a product online and buy it in a physical store.
- 53% envision themselves doing the opposite: viewing products in-store and buying it online.
- 55% of consumers want to browse products online and check what’s available in local stores.
- Over50% of adult shoppersuse BOPIS, with 67% adding extra items to their carts when they can pick them up immediately.
Brands investing in brick-and-mortar retail include Canadian fashion brandSMYTHE, which opened its store in Toronto. After years of experimenting with pop-up shops, Gymshark also opened itsfirst permanent flagship storein central London.
“A children’s wear retailer I spoke to pivoted from in-store events to virtual shopping events via Zoom during COVID,” says Kyle Monk, Director of Insight forBritish Retail Consortium.
“Suddenly, they were having one member of staff walking around the store selling products to two to 300 people per call every week, instead of just a few in person. Retailers who thought innovatively and pivoted thrived over the last period.”
这是no wonder 53% of brands are investing in tools that allow them to sell anywhere.
Iconic streetwear retailer Culture Kingsopened an experiential, 14,000-square-foot store in Caesars Palace on the Las Vegas Strip in October 2022. Culture Kings is prioritizing a "retail-tainment" approach to physical retail, featuring a recording studio, Secret Room, and other immersive experiences. The company plans to open additional experiential stores in key US cities.
7. Investments in YouTube Shorts
Move over TikTok: Short-form video platform YouTube Shorts is gaining traction among fashion brands and creators. According tosocial media leads, YouTube Shorts offers a first-mover advantage similar to early TikTok adopters.
品牌如耐克、丢弃,美国鹰有一个lready added Shorts to their marketing mix. Luxury brands like Gucci, Christian Dior, and Louis Vuitton are also getting on board.
Shorts see more than 30 billion daily views and attract 1.5 billion monthly users, according to YouTube. With these numbers, fashion brands can gain YouTube subscribers without investing in long-form video, receive high engagement rates, and boost sales.
Shopify and YouTube are teaming up to give merchants and creators a powerful new way to connect to consumers, build their businesses, and share their stories. With the launch of YouTube Shopping on Shopify, merchants can easily integrate their online store with one of the world’s biggest entertainment platforms.
Learn moreabout YouTube Shopping.
8. Expanding into repair services
Fixing items rather than throwing them away is becoming a trend for fashion brands. Bottega Venetarecently announcedthat it’s giving all customers a lifetime warranty on their handbags. Louis Vuitton will alsorepair any bagfor a price, depending on the item and type of repair.
The expansion into repair services comes at the helm of sustainability. The fashion industry is becoming more aware of its environmental impact, and repairs are a cost-effective way to keep clothes in good condition longer.
Brands like Patagonia and Arc’teryx have opened repair centers, as have fast fashion retailers like Zara and Uniqlo. Repair-focused startups like The Restory haveraised millionsto date as interest in sustainable fashion and resale boosts demand to extend the life of garments.
9. The shift to wholesale
Inflation, supply chain issues, and lack of consumer spending is pushing DTC brands toward wholesale. A recentGlossy and Modern Retail surveyshows that DTC brands are investing in other types of sales partnerships to diversify income.
When asked about performance over the past 12 months, 62% of respondents said wholesale revenue increased the most, even compared to direct sales. Brands see wholesale as a major business component moving forward too, with 80% predicting wholesale revenue will go up over the next year.
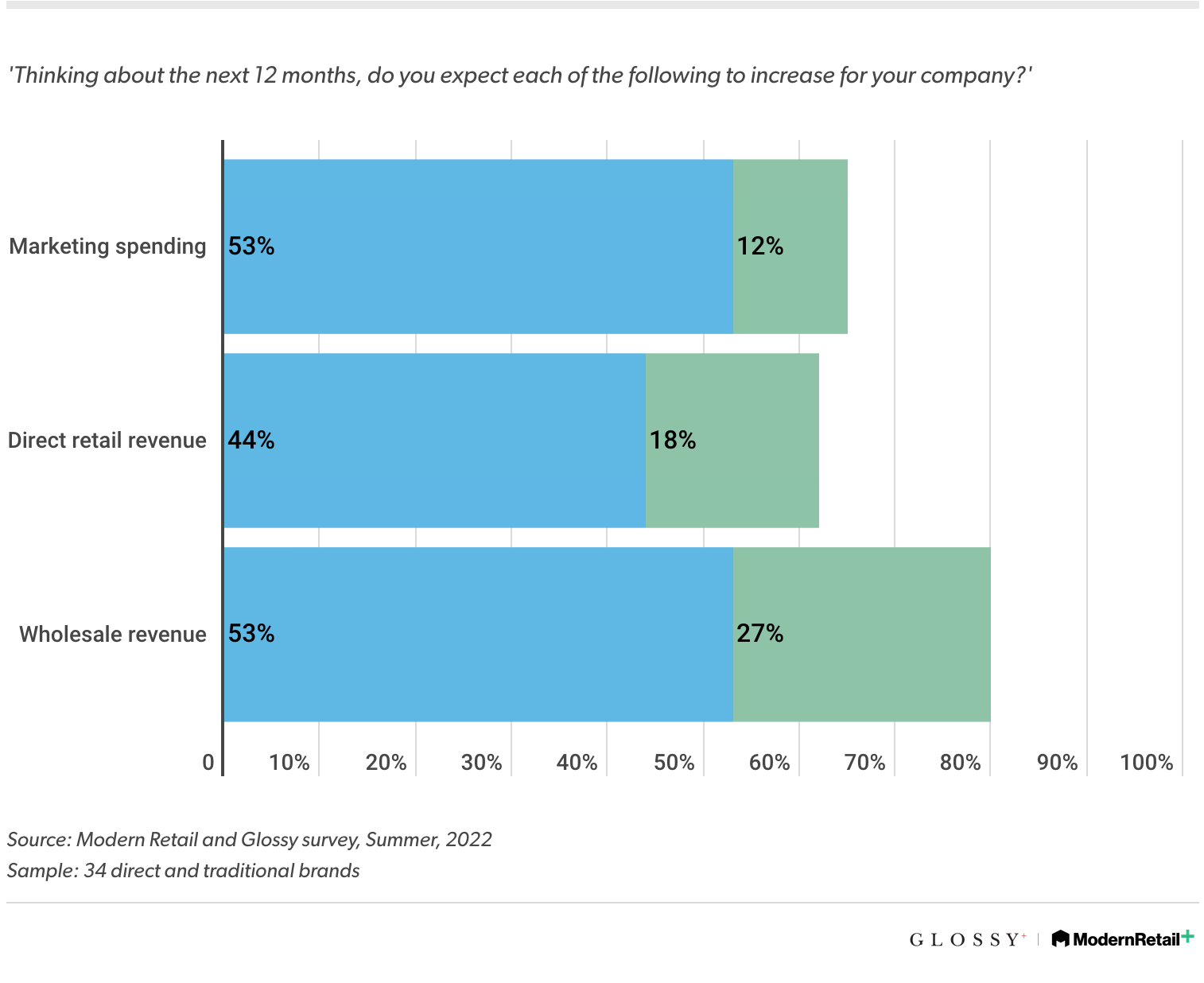
Source:Glossy
Digitally-native-seeking retail partnerships isn’t a new thing. Harry’s entered Target in 2016. DTC brands like Quip and Native followed suit into big-box retailers shortly after.
But 2023 marks a turning point for DTC brands rushing into wholesale. Sales are up at mass retailers like Target and Walmart. Ongoing supply chain disruptions are making direct channel fulfillment increasingly harder, harming profits.
So while the pressure to grow may be intense, there are still opportunities for DTC brands to find success. Wholesale partnerships may become essential for survival in coming years as DTC brands navigate the turbulent economic landscape.
Ecommerce fashion statistics
According to Statista, the ecommerce fashion industry’s compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is tipped toreach 14.2%between 2017 and 2025, with the industry hitting a$1 trillionvaluation by 2024.
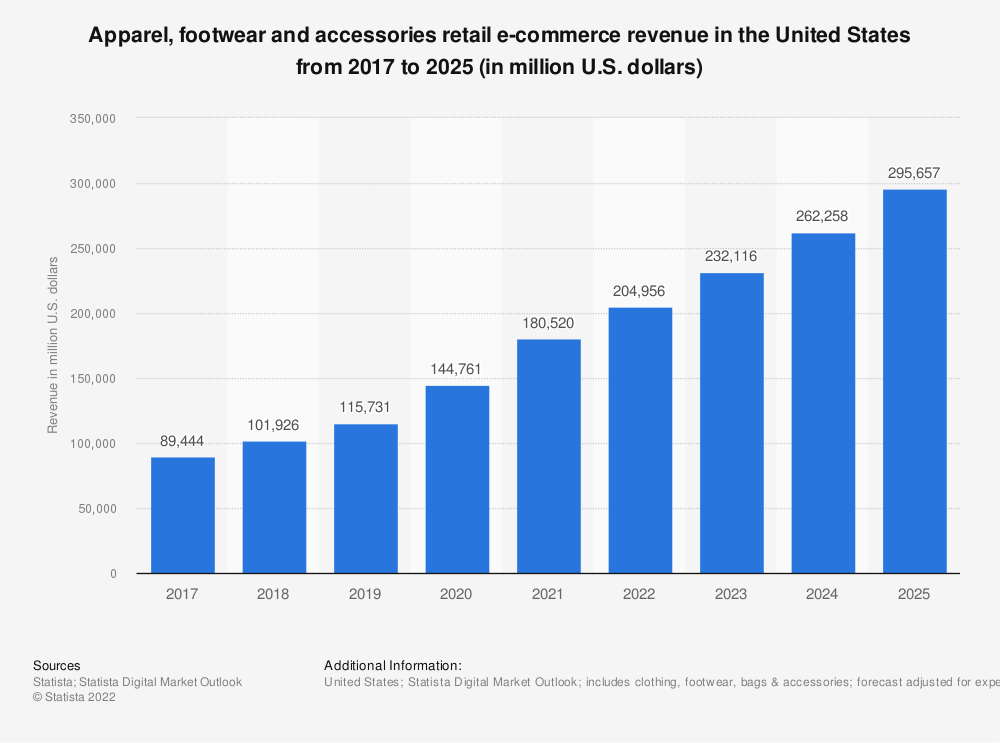
Sales of apparel, footwear, and accessories continue to rise, hitting$204.9 billionin the US alone. That’s tipped to grow by 13% this year, with consumers set to spend $204.9 billion on fashion items online.
推动这种增长是四个明显的机会:
- Expanding global markets outside the West
- Increasing online access and smartphone penetration
- Emerging worldwide middle classes with disposable income
- Harnessing the power of celebrity and influencer culture
The biggest threats to established brands include:
- The death of brand loyalty due to market saturation
- Pressure from consumers to use ethically sourced and green manufacturing materials
- Technological advancements with virtual worlds, such asNFTs and the metaverse
We’ll get into strategies to combat these issues later. For now, let’s examine how these big numbers play out in industry sub-verticals.
1. The COVID impact
The COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on the last few years’ fashion ecommerce predictions. When lockdowns were enforced globally in March 2020,27% of US consumerssaid they planned to spend “somewhat” or “a lot” less on luxury and fashion items than they had budgeted prior.
Despite this,McKinsey named itthe “perfect storm for fashion marketplaces.” Brands likeZalandoreported a 32% to 34% growth in gross merchandise value (GMV) during the second quarter of 2020. Fast-fashion brand Shein saw its valuationdouble, to $30 billion, making it the world’s largest online-only fashion retailer.
One branch of fashion retail that has taken off is athleisure.Athleisure’s market sizewas valued at $155.2 billion in 2018—a figure that’s set only to rise.
Casualwear remainsdominant on Amazon, with athleisure predicted to have a CAGR of 6.7% from 2019 to 2026 and reach $257.1 billion. The loungewear and sleepwear market shows similar signs of growth, poised to increase by$19.5 billionbetween 2020 to 2024.
The result? Fashion brands with an ecommerce store maintain a stronghold in athleisure style goods, like Nike and Lululemon, have reported incredible growth over the course of the pandemic.
2.服装和服装
Lower digital barriers to entry for all clothing merchants offer the opportunity to market, sell, and fulfill orders globally and automatically. As a result, worldwide revenue and revenue per user (ARPU) are both projected to grow.
In the US alone, the apparel and accessory industries accounted for29.5% of all ecommerce salesin 2021. In Europe, it’s expected that by 2025, each consumer willspend $999on fashion-related items over the course of a year.
3. Shoes segment
As a segment of ecommerce fashion, the shoe industry saw similar peaks in market value. In global market size, thefootwear segmentwill increase from $365.5 billion in 2022 to $530.3 billion in 2027.
Asia is dominating this segment,holding 54%of the global footwear market (compared to just 14.8% for Europe and North America, respectively).
Athletic footwear is also a growing segment, tipped to generate$63.5 billionin 2023—a 23% increase from the $51.4 billion valuation in 2020.
4. Accessories and bags
Not surprising, the bags and accessories segment—although still growing at a stronger rate—will likewise see double-digit growth. The fashion accessory segment will have aCAGR of 12.3%between 2016 and 2026, with Asia-Pacific being the fastest growing market.
Those projections actually make bags and accessories one of the healthiest segments of ecommerce fashion, despite its absolute numbers being the smallest.
5. Jewelry and luxury
In 2020, the global jewelry market was valued at a total of$228 billion. It’s forecasted to reach $307 billion by 2025, with ecommerce sites expected to facilitate20.8% of salesin the luxury goods category this year. Luxury watches are set to take a huge slice of that revenue—customers will spend$9.3 billionon them in 2025.
The growth (despite coronavirus-related recessions) mirrors other financial crises.McKinseypredicted that consumers will “return more quickly to paying full price for quality, timeless goods, as was the case after the 2008–2009 financial crisis.”
Increasing affluence in Asia-Pacific and in the Middle East drove up the average revenue per luxury good consumer to $313. Despite luxury goods sales seeing sluggish growth, at 3.4% annually,McKinseyforecasts indicate that ecommerce could triple in sales over the next decade—reaching €70 billion ($79.5 billion) by 2025.
The biggest threat is the affordable luxury market: Should the industry offer luxury goods at multiple price points to grow the market overall? Or will affordable luxury dilute or erode the high-end luxury market—dampening consumer confidence that what they are buying is “true luxury”?
Want more about the state of ecommerce fashion?
The state of ecommerce fashion is developing more quickly than ever. What worked two years ago is outdated now—largely due to consumer preferences changing, values becoming integral to the purchase decision, and footfall returning to brick-and-mortar stores.
Fashion Ecommerce FAQ
What is fashion ecommerce?
Fashion ecommerce is the selling and buying of fashion and apparel online. The fashion ecommerce industry is a highly competitive space where stores will try various marketing methods to stand out.
How big is the fashion ecommerce market?
According to Statista, the ecommerce fashion market is estimated to be US$752.5 billion in 2020. The market is expected to grow by 9.1% each year.
Is fashion ecommerce the largest ecommerce market segment?
Yes, fashion ecommerce is the largest B2C ecommerce market.
Read More
- The Hundreds Creates Culture, Content & (Then) Commerce: Streetwear Fashion
- Direct-to-Consumer Business Model in CPG: How-To Guide for Brand Managers
- Social Commerce Strategy: Improve Your Social Selling With These 9 Best Practices
- Brands Building Community During COVID-19
- 10教训增长最快的消费选择ronics Websites
- The Giving Economy: How Consumers Are Paying It Forward to Retailers
- What Game Designers Can Teach You About Influencing Buying Behavior






